SEO isn't all about key-word optimized content and link building. At the heart of SEO is user experience. This is where UX design comes in.
With all of the advice available today on SEO, it can be hard to know the best approach to gaining site rank. Not only do you need to navigate Google’s zoo of algorithm updates, but you must also understand the hundreds of ranking factors that come into play when Google is determining where your site ranks. Even the most experienced SEO’s don’t focus on every single ranking factor, so don’t feel too overwhelmed if you are just getting started. The truth is that some ranking factors are weighted more heavily than others, and those should be your main priority.
You already know the most heavily weighted ranking factors include keyword-optimized content and link building, however, that’s not the heart of SEO. In fact, that’s a very common misconception that many SEO’s have. The heart of SEO is actually user experience. This is where UX Design comes in.
What is UX Design?
To put it simply, user experience (UX) refers to the interactions that someone has with a company, product, service, or in our case, a website. The goal of UX design is to create a seamless and enjoyable experience throughout every aspect of the user’s journey. So whether the user is being guided through the checkout process, or just catching up on the latest blog post, the experience should be the same; a positive one.
If you’ve read anything about UX already, you know it often doesn’t come alone. UX is generally paired in discussion with UI. This makes sense as UX and UI tend to go hand in hand, especially where websites are concerned. Many people often get UX and UI confused, but in reality, they are quite different. User Interface (UI) design refers to the graphical layout of an application. This encompasses everything from typography, buttons, color scheme, and any other type of visual element.
Notice the difference? UI is visual, UX is functional. Together they create a dynamic duo that when used effectively, will create a positive experience for any user. Although we recommend focusing on both UI and UX, today we want to primarily cover the functionality aspects of a website.
So what exactly does this have to do with SEO?
As we mentioned before, user experience is at the heart of SEO. Google continues to put an emphasis on user experience, and many of the latest algorithm updates prove this trend will continue in the future.
Take RankBrain for example. This algorithm update uses UX signals to determine how satisfied a user is with the results they were given. RankBrain monitors how you interact with the search results and will either boost or drop a particular page depending on the signals you provide.
Let’s look at an example:
Say that you are looking to help your cat lose weight. You, like most people, will click on the first organic result shown.

Maybe the site was taking too long to load, maybe the information was presented in a large block of text that you don’t really have the time to read through, or maybe you were continually interrupted with various pop ups while on the page, whatever the reason was, you leave and decide to click on the second listing instead.
This one loads much more quickly and has content formatted in a way that’s easy to digest. We stay here much longer than the first listing, then proceed to exit the site once we’ve finished reading the page.
RankBrain is constantly interpreting signals like the example above, and adjusting the search results as needed. If enough people are bouncing off the first listing and lingering on the second, RankBrain would use those signals to move the second listing into the first position.

So moving back to SEO, how can we leverage UX Design to help send the right signals to algorithms such as RankBrain?
UX Strategies That Impact SEO

UX and SEO have a lot in common. Both aim to make the user happy. SEO wants to make users happy by helping them find the information they are searching for, UX wants to make sure that they can easily find the information once they land on a website. Here are a few strategies that both impact UX and SEO:
Site Speed
It’s no secret that website speed has long been a ranking factor. It continues to be very important, as even a 1-second delay in page load time can cause your conversions to decrease by 7%. In fact, if that delay happened to occur on Amazon, they would lose $1.6 Billion in sales.
When it comes to site speed, every second counts. The less interactive a website becomes, the more likely it is that they will leave and click on a competitor’s site instead. The good news is that there are a lot of resources out there to help you improve your site speed. First, you will want to see how your site currently scores by using the free Google PageSpeed Insights tool:
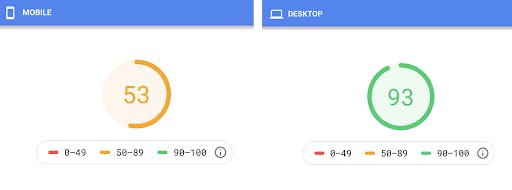
This tool will show you speed scores for both desktop and mobile, as well as actionable suggestions on how you can make both versions faster:
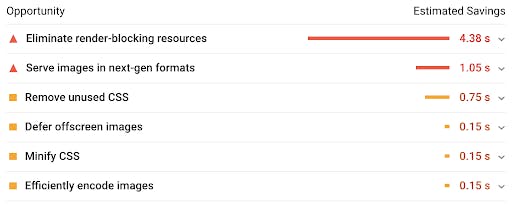
You can expand on the items to get further instructions on what they mean. Some other simpler ways to improve on your website speed are:
- Compressing high-quality images, and cropping if needed
- Remove auto-play media formats
- Get reliable hosting
- Consider a CDN (content delivery network)
- Utilize lazy loading
- Browser caching
Your goal is to have a loading time of 2 seconds or less. This will create a positive experience for users and send all the right signals to algorithms like RankBrain.
Bounce Rate
It can sometimes be difficult to pin down exactly why people abandon a website or a particular page. The content might not be relevant to the searcher’s query, the site might load too slow, or the overall layout might be confusing and hard to navigate. Whatever the reason may be, having a bounce rate isn’t something you need to be overly stressed about. The average bounce rate for a website is actually around 40% or less.
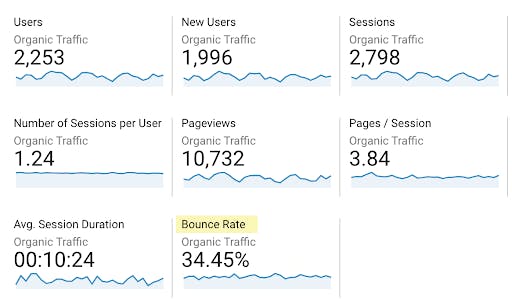
Determine which pages on your site have the highest bounce rate, then from there determine what you can do to bring the bounce rate down, especially if it’s a page that should be driving conversions. Apart from making your website faster, you can focus on the formatting of your content. People don’t want to read large blocks of text, so breaking it up with images, various subheadings, bullet points, and more, will help make it more approachable.
Another thing to focus on when it comes to copy is relevancy. If you are trying to rank for a specific search term, you need to make sure you understand the searcher’s intent and have content relevant to match that intent. Irrelevancy continues to be one of the highest contributors behind bounce rate.
Average Session Duration
Bounce rate isn’t the only thing you should keep an eye on. You’ll also want to see how much time users are spending on average on your website. The more valuable and engaging your content is, the longer a user will spend consuming that content. This, in combination with bounce rate, is a great way to determine what’s working on your website and what needs to be improved. If you notice that a page has a particularly high session duration, see what’s different about that page compared to other pages.
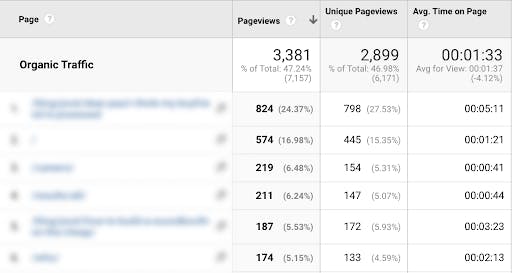
If you feel that your session duration is too low, there are various ways you can go about improving it:
- Add videos: adding various types of content, like videos, is a great way to get a user engaged. However, make sure that videos are properly set up on the page, otherwise, you’ll drastically hurt your site speed.
- Add Images: Images are a great way to break up long blocks of text, which makes the page more readable.
- Utilize additional tools: Sometimes to further understand where the issue lies, you need to know exactly where on a page users are losing interest. Using heatmap tools is a great way to help you understand how users interact with your page.
- Format correctly: Breaking up content with subheadings, short paragraphs, bullet points, etc. These all make the content easier to scan and not feel so overwhelming for a user.
There are many more ways to help increase session duration, but implementing just a few of the above items will make a big difference.
Site Navigation
Many people make the grave assumption that users will always enter through their home page. This is simply not true. A user can enter the site through virtually any page, which means that they also need to be able to navigate the site smoothly from any page.
The more simplified you can make your navigation process, the better experience it will be for a user and website crawlers. Minimize the use of popups, proving long lists of menu options, or leading to dead ends. This can be challenging the larger your website starts to grow, but it’s a very important element to creating a good user experience.
In fact, by having a clean navigation structure, you may have sitelinks displayed in the search results, which helps to increase your CTR:

Google only shows sitelinks when they feel they will be useful to a user. So, if your website structure isn’t easy for search crawlers to navigate, they won’t be able to find potential sitelinks to show to users.
Final Thoughts
There are many more UX design strategies that play a significant role in SEO, and although we won’t cover every single one today, we encourage you to take UX and UI seriously when it comes to your website.
Google strives to create positive user experiences, and you want to please Google so you can bring more traffic to your website. The more time and attention that you pour into small details, like functionality and overall usability of your website, the more you’ll be favored by Google. When analyzing your website, don’t just focus on SEO. Remember, your website was created for one thing: Users. So embrace UX and put users at the forefront of your strategy.

